The story of Katie Standon, better known as “Genie,” is one of the most profound and tragic cases in child psychology and linguistics. Genie, born Susan Wiley in 1957, endured unimaginable neglect during her early years. Locked in isolation by her father, she became the subject of intense scientific research after her discovery in 1970. The questions about her whereabouts and well-being continue to intrigue many. Where is Katie Standon (Genie) now in 2024? Let’s dive into her life, the impact of her case, and her current situation.
The Early Years of Genie: A Life of Extreme Abuse
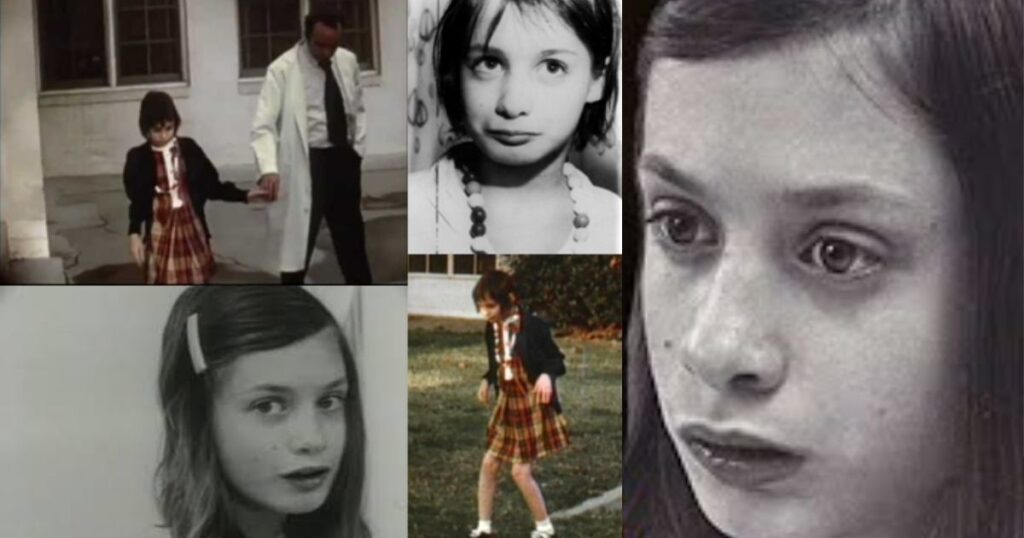
Genie’s household overflowed with dysfunction and abuse. Her father, Clark Wiley, labeled her as mentally disabled and isolated her entirely from the outside world. Starting at 20 months old, Genie spent her days in a small room, tied to a potty chair or trapped in a crib. She experienced no social interaction, verbal communication, or physical freedom.
Her physical and mental development suffered immensely. When authorities discovered her in 1970, at the age of 13, she was malnourished, unable to speak, and severely delayed in motor and cognitive skills. Her plight shocked the world and attracted the attention of psychologists, linguists, and social workers, who saw her as a rare opportunity to study the effects of severe isolation and neglect on human development.

The Discovery: How Genie Became a Research Subject
In 1970, Genie’s mother escaped her abusive husband and sought help from social services. Authorities quickly realized the extent of Genie’s abuse and intervened. Her discovery led to widespread media coverage, and she was soon placed in protective custody. Psychologists and researchers saw Genie’s case as an unprecedented opportunity to study the “critical period hypothesis” in language acquisition.
The critical period hypothesis states that the human brain learns language most effectively within a specific window of time. Genie’s situation stood out because she had passed this critical period without any exposure to language. Researchers studied her progress to answer fundamental questions about human development. Researchers hoped that studying her progress would provide answers to fundamental questions about human development.
Research Years: Progress and Controversies
After her rescue, Genie was placed under the care of researchers who worked to help her regain basic skills and document her development. During this period, she showed remarkable progress in some areas:
- Communication Skills:
Genie began to develop a vocabulary, learning individual words and simple phrases. However, she struggled to construct grammatically correct sentences, supporting the idea that language acquisition is limited after the critical period. - Physical Rehabilitation:
With therapy, Genie gained strength and improved her motor skills. She learned to walk more confidently and explore her environment. - Social Interaction:
Despite her past isolation, Genie showed a curiosity about the world and people around her. She formed bonds with some of her caretakers and researchers.
However, her time in research care was not without controversy. Critics argued that the intense focus on studying Genie sometimes overshadowed her need for emotional stability and long-term well-being. Ethical concerns about her treatment during this period remain a topic of debate in psychology.
The Later Years: Life After Research
By the late 1970s, funding for Genie’s care and research ended. This left her without the support of the team that had been caring for her. She was briefly returned to her biological mother’s care, but the arrangement did not last due to her mother’s inability to meet Genie’s complex needs.
Over the next several years, Genie was placed in various foster homes. Unfortunately, some of these placements exposed her to further abuse and neglect, causing her to regress. The lack of a consistent, supportive environment undid much of the progress she had made during the research years.
Where is Genie Now in 2024?
As of 2024, Genie is 67 years old and resides in a private care facility in Southern California. Her exact location is kept confidential to protect her privacy. Here’s what is known about her current life:
- Living Conditions:
Genie is well-cared for in a state-run facility that specializes in individuals with severe developmental disabilities. Reports suggest that she is content in her environment, though she remains largely non-verbal. - Health and Well-Being:
Genie has physical and mental health challenges resulting from her early years of abuse and isolation. She has limited communication abilities but appears to enjoy simple routines and interactions with caregivers. - Public and Family Contact:
Genie’s contact with the outside world is minimal. Her family has largely remained distant, and legal guardians ensure her privacy is respected.

How Genie’s Case Changed Research Ethics
Genie’s case raised numerous ethical concerns about how vulnerable individuals are treated in scientific studies. These concerns have had a lasting impact on the development of ethical research standards.
| Aspect | Lessons from Genie’s Case |
|---|---|
| Informed Consent | Genie was unable to give consent, highlighting the importance of obtaining appropriate legal consent. |
| Prioritizing Welfare | Critics argued that researchers prioritized their studies over Genie’s well-being, leading to stricter regulations. |
| Confidentiality | Public fascination with Genie led to media exposure, emphasizing the need for protecting participants’ privacy. |
| Ethical Oversight | Genie’s case underscored the necessity of ethical review boards to ensure research benefits participants. |
| Balancing Research Goals | The focus on scientific discovery must not overshadow the subject’s basic rights and emotional needs. |
This table summarizes the ethical lessons drawn from Genie’s story, which continue to influence how research involving vulnerable populations is conducted today.
Read To Know About: Urlebird: Your Gateway to Anonymous TikTok Viewing
The Impact of Genie’s Case on Science
Genie’s story has had a lasting impact on the fields of psychology, linguistics, and child development. Some of the key contributions include:
- Critical Period Hypothesis:
Genie’s case provided strong evidence that language acquisition is heavily dependent on early exposure during a critical developmental window. - Understanding Social Isolation:
Her experiences shed light on the devastating effects of extreme neglect on cognitive and emotional development, influencing child welfare policies worldwide. - Ethical Standards in Research:
The controversies surrounding Genie’s care highlighted the importance of prioritizing the well-being of research subjects. Her case led to stricter ethical guidelines in psychological studies.
Also Read: 10 Big Lip Cartoon Characters of All Time
Lessons Learned from Genie’s Case
While Genie’s story provided invaluable insights into human development, it also serves as a cautionary tale. Some of the lessons include:
- Balancing Research and Care:
Researchers must prioritize the emotional and physical well-being of subjects, especially vulnerable individuals like Genie. - The Role of Early Intervention:
Genie’s case underscores the importance of early social interaction and language exposure in a child’s development. - Protecting Privacy:
The intense media coverage and public interest in Genie’s case raised questions about her right to privacy. Efforts to shield her identity in her later years reflect the importance of respecting individuals’ dignity.
The Legacy of Genie’s Story
Genie’s story remains one of the most poignant examples of resilience in the face of unimaginable adversity. It has inspired countless studies, documentaries, and books, keeping the discussion about early childhood experiences and their long-term effects alive. At the same time, her case has become a reminder of the ethical complexities involved in research on vulnerable populations.
Timeline of Genie’s Life: Key Events
Below is a timeline highlighting the major events in Genie’s life, from her early years of abuse to her current situation in 2024:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1957 | Genie (Susan Wiley) is born in California. |
| 1958-1970 | Genie is confined to a small room, enduring severe neglect and abuse by her father. |
| 1970 | Authorities discover Genie at the age of 13, malnourished and unable to speak or walk properly. |
| 1971-1975 | Researchers begin studying Genie, focusing on language acquisition and social development. |
| 1977 | Funding for Genie’s research ends, and she is placed in foster care. |
| 1980s | Genie regresses after experiencing further neglect in some foster homes. |
| 1990s | Genie’s legal guardians secure her placement in a private care facility. |
| 2024 | Genie, now 67 years old, resides in a private care facility in Southern California. |
This timeline provides an overview of the significant moments in Genie’s life, illustrating her journey from abuse to relative stability in her later years.
Conclusion
Where is Katie Standon (Genie) now in 2024? Genie resides in a private care facility in Southern California, living a life far removed from public attention. Her story, while tragic, has left a lasting legacy in science and society, offering insights into human development, the effects of neglect, and the importance of ethical research practices. Though her early years were marked by unimaginable hardship, Genie’s resilience continues to inspire discussions about compassion, care, and the critical role of nurturing in human growth.
Also Read: 11 Big Chin Cartoon Characters of All Time
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who is Genie (Katie Standon)?
Genie, born Susan Wiley, is a child abuse survivor discovered in 1970 after enduring extreme isolation for over a decade. Her case became pivotal in language development research.
2. Why was Genie referred to as the “Wild Child”?
She was called the “Wild Child” due to her severe isolation, lack of language skills, and feral behavior, which resembled cases of children raised without human contact.
3. What happened to Genie after her rescue?
Genie was placed under the care of researchers who studied her language acquisition and development. Later, she moved between foster homes and eventually to a care facility.
4. What did researchers learn from Genie?
Genie’s case supported the critical period hypothesis, showing that language acquisition is heavily influenced by early exposure during developmental windows.
5. Why did Genie stop being studied?
Research funding ran out in the late 1970s, and ethical concerns arose about prioritizing research over Genie’s emotional and physical well-being.
6. Where is Genie now in 2024?
Genie is 67 years old and resides in a private care facility in Southern California, away from public attention to ensure her privacy and safety.
7. How did Genie’s case change research ethics?
Her treatment raised concerns about the balance between research goals and participant welfare, leading to stricter ethical guidelines in psychological studies.
8. What were the long-term effects of Genie’s isolation?
Her isolation caused severe developmental delays, including limited language skills, cognitive deficits, and lifelong dependence on caregivers.
9. Did Genie ever fully recover?
No, Genie made some progress in language and socialization but never fully recovered from the effects of her early isolation and trauma.
10. Why is Genie’s story important today?
Genie’s story highlights the importance of early childhood experiences in development and continues to influence research on language, trauma, and ethics.
